Diabetic Retinopathy in 2025: Modern Strategies to Protect Vision
Diabetic Retinopathy in 2025: Modern Strategies to Protect Vision
In 2025, diabetic retinopathy (DR) remains a leading cause of vision loss among adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes. However, thanks to recent advances in ophthalmology and diabetes care, patients now have more options to detect, prevent, and treat this serious eye complication.
1. AI-Powered Retinal Screening
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing how DR is diagnosed. In 2025, AI-assisted fundus photography allows for fast, accurate screening even in primary care clinics or pharmacies.
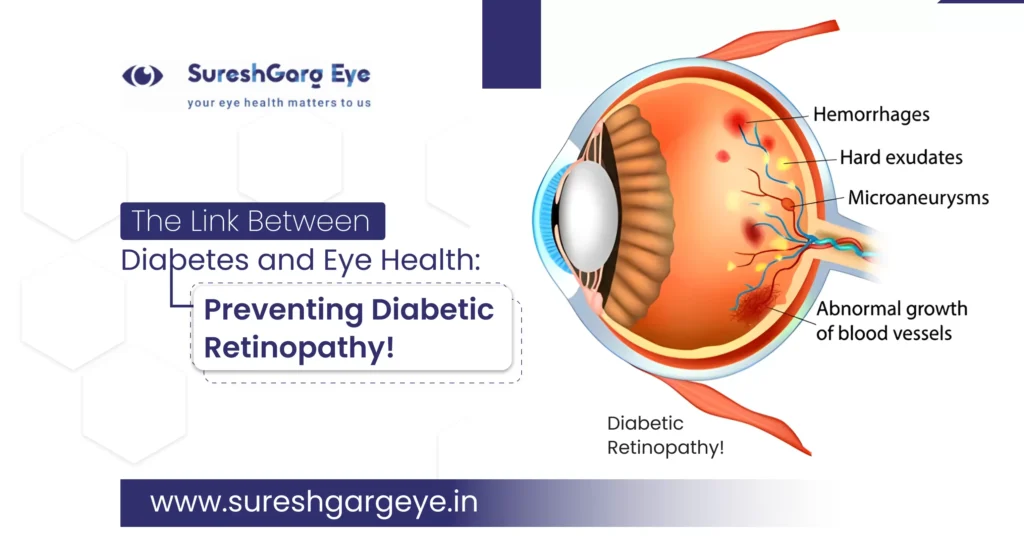
These tools analyze retinal images in seconds and flag early signs of microaneurysms, hemorrhages, or neovascularization—long before vision is affected.
2. Wearable Glucose Monitoring for Eye Protection
Tight blood sugar control is essential to prevent DR. Today’s diabetic patients benefit from continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) integrated into wearable tech or smart lenses.
These devices alert users and healthcare providers when sugar levels spike, reducing the chances of retinal capillary damage that leads to DR.
3. Anti-VEGF Injections: Still the Gold Standard
In cases where DR has already developed, anti-VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor) injections remain the most effective treatment. These drugs reduce abnormal blood vessel growth and fluid leakage in the retina.
Newer formulations in 2025 allow for longer dosing intervals—as little as one injection every 3–4 months—improving patient comfort and outcomes.
4. Laser and MicroPulse Therapy
In advanced or proliferative DR, laser photocoagulation is still used to seal leaking vessels. However, 2025 has seen a rise in MicroPulse laser therapy, a less damaging alternative that protects surrounding tissue.
These techniques are now guided by high-resolution OCT imaging for pinpoint precision.
5. Future Therapies: Gene and Stem Cell Approaches
Experimental treatments in 2025 include gene therapy to suppress abnormal vessel growth and stem cell injections to regenerate damaged retinal tissue.
Though still in clinical trials, early results are promising, especially for patients with macular edema or severe retinal ischemia.
Conclusion
In 2025, diabetic retinopathy is more manageable than ever before. With help from AI, smart glucose tools, improved medications, and emerging therapies, patients have a real chance to preserve their sight.
Regular screening, early intervention, and personalized care remain the pillars of successful treatment.
Keywords: diabetic retinopathy 2025, AI retina scan, anti-VEGF injections, glucose monitoring eyes, laser therapy for DR, retina damage diabetes, new treatments for diabetic eye disease.